--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Scenario 1: ABAP – ABAP
Two SAP systems – actually two AS ABAP systems - communicate with each other. Here, the data exchange between the two partner systems is made via the RFC interface. An additional conversion of the data format is not necessary.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There are four different scenarios:
- AS ABAP - AS ABAP
- AS ABAP – External system
- AS ABAP - SAP Java
- AS ABAP – External Java system
Scenario 1: ABAP – ABAP
Two SAP systems – actually two AS ABAP systems - communicate with each other. Here, the data exchange between the two partner systems is made via the RFC interface. An additional conversion of the data format is not necessary.
Scenario 2: ABAP – External System
In this scenario, the partner system is not an SAP system: Here, the RFC API is used to implement an interface that converts the ABAP data format
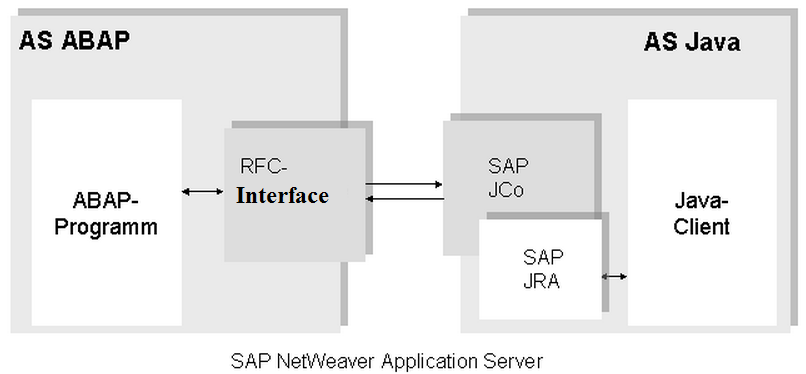
Scenario 3: ABAP – Java (SAP)
In this scenario, the communication does not have to be between two separate systems. However, the RFC interface is also required for communication between AS ABAP and AS Java within the SAP NetWeaver Application Server. At the AS Java end,SAP JAVA Connector performs the interface function and is responsible for mapping the ABAP-Java data types. SAP JCo is lagged by SAP JAVA Resource Adapterr, which is based on the JAVA EE standard architecture.
Scenario 4: ABAP – Java (Non-SAP)
Here, AS ABAP communicates with a Java system that is not based on SAP AS Java. In this scenario too, SAP JCo performs the interface function and data mapping for the non-SAP Java system
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------



No comments:
Post a Comment